 LogisticForecast
LogisticForecast
Syntax
LogisticForecast(Year1, Value1, Year2, Value2,... YearN, ValueN) or
LogisticForecast(ExcelFile, ExcelRange)
LogisticForecast(LCDS, SeriesName, Filter1, Filter2, [CountryISO3])
LogisticForecast(Branch:Variable)
See also: Using Time-Series Functions and Specifying Excel File and Range Parameters.
Summary
Logistic forecasting is used to estimate future values based on a time series of historical data. The new values are predicted using an approximate fit of a logistic function by linear regression.
A logistic function takes the general form:
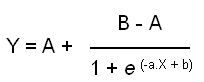
where the Y terms corresponds to the variable to be forecast and the X term is years. A, B, a, b are constants and e is the base of the natural logarithm (2.718). A logistic forecast is most appropriate when a variable is expected to show an "S "shaped curve over time. This makes it useful for forecasting shares, populations and other variables that are expected to grow slowly at first, then rapidly and finally more slowly, approaching some final value (the "B" term in the above equation).
Use this function with caution. You may need to first use some other package to test the statistical validity of the forecast (i.e. test how well the regression "fits" the historical data).
NB: The result of this function will be overridden by any value calculated for the base year of your analysis. In some cases this may lead to a marked "jump" from the base year value to the succeeding year's value. This may reflect the fact that the base year you have chosen is not a good match of the long-term trends in your scenario , or it may reflect a poor fit between the regression and the historical data.
The second syntax of the function retrieves years and values from a specified Excel file and range. The third syntax of the function retrieves years and values from the online LEAP Cloud Data Server (LCDS). In both cases, retrieving this data initially may takes some time (typically a second or less depending on your internet connection), but thereafter values are cached locally for near-instant retrieval. Use the Time-Series wizard to help specify the parameters required when using these syntax.